Kemp Design Model (proposed by Kemp, Morrison, and Ross) is a design strategy that takes a non-traditional approach to eLearning development and follows a cyclical structure. Every aspect of the eLearning course design and learning process is taken into consideration (e.g. Support or project management that are not present in some other models). It adopts a circular, flexible structure, and allow entering the process pretty much at any of the main nine points.
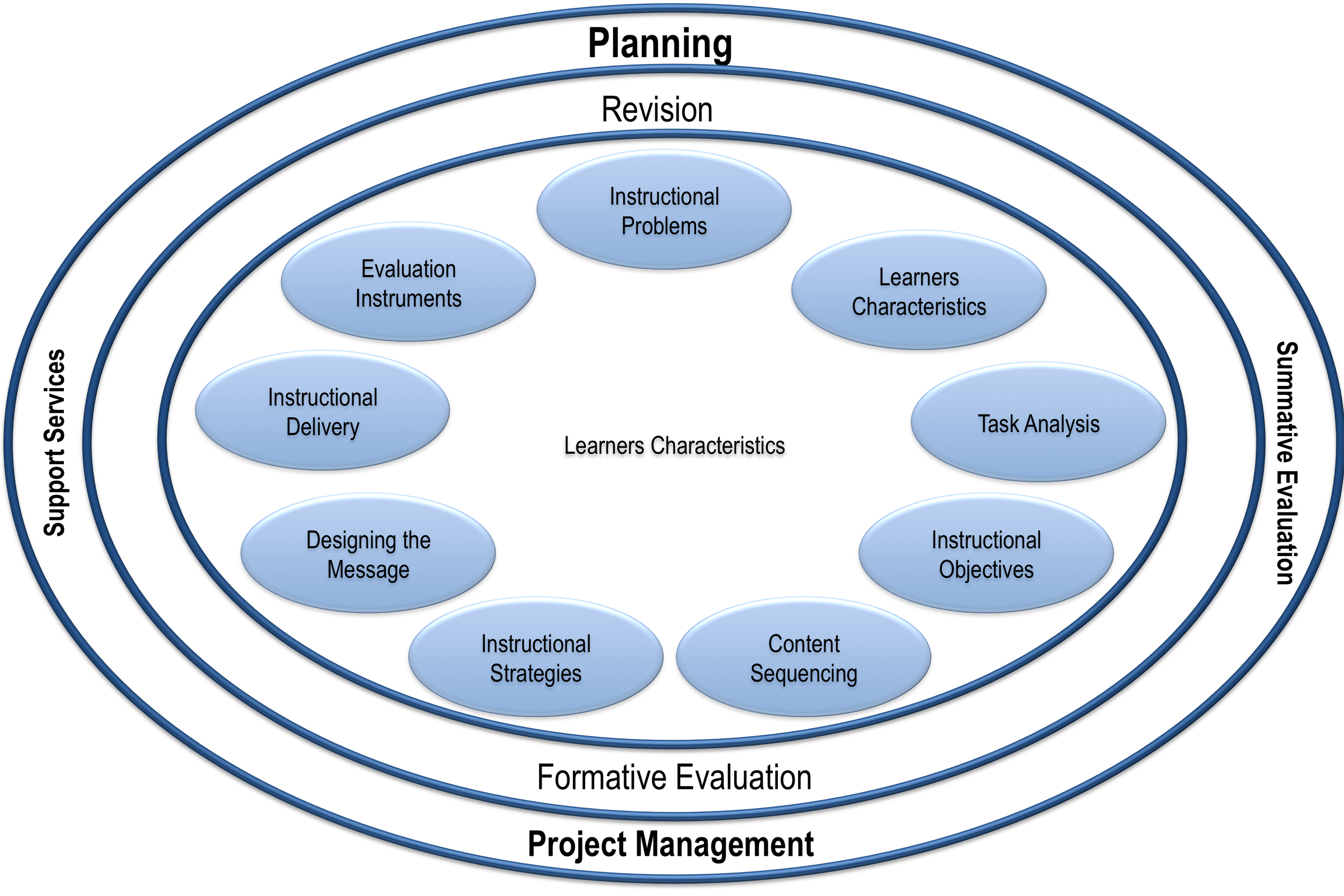
- Determine the specific goals, and also identify potential instructional issues (define the learning outcomes for the course, what is that the learners need to learn or the skills they need to acquire (what broad concepts, new knowledge, or course-specific content should learner acquire? what tasks should the learner be able to perform and skills demonstrate?)
- Identify characteristics of learners that should be taken into account during the planning process – focuses on learning styles and needs of learners and cognitive load related to topics, tasks, and procedures.
- Clarify course content, and analyze the proposed task components in relation to the stated goals and purposes of the course – helps the designer to begin thinking about the overall content of the course in relation to the characteristics of the learner (similar to the third stage of Dick and Carey model and analysis stage in the ADDIE model)
- Define instructional objectives and desired learning outcomes – content and task analysis, which is focused on the whole learner, and the required depth of understanding of new material. Bloom’s taxonomy is helpful here.
- Ensure that content for each instructional unit is structure sequentially and logically to facilitate learning – deals with examining the course ILOs – the designer analyzes the broad learning objectives of the course, and translates them into more specific and defined goals (similar to the first stage in the Dick and Carey model).
- Design instructional strategies to enable individual learners to master the content, and achieve desired learning outcomes – the design of activities that will assist in course facilitation.
- Plan the instructional message and the appropriate mode of delivery – deciding on instructional resources necessary to allow teachers to effectively teach, and students to effectively learn
- Develop evaluation instruments suitable for measuring and assessing learners’ progress towards achieving course objectives – takes into account support services that are available, or that may be required, to facilitate both teaching and learning activities (unique in the Kemp model)
- Choose the appropriate resources that will support both teaching and learning activities – deals with formative and summative evaluations and assessment models.
More about this model can be found here
A simple example of practical application of the KEMP instructional design model can be found at the eLEarning industry blog.